You’ll find that the politics behind Universal Basic Income are surprisingly diverse. Support spans from progressives emphasizing poverty reduction to some conservatives interested in economic stability and automation’s impact. Demographic and cultural views influence opinions, with younger, lower-income groups often more open to UBI. Despite deep ideological divides, surprising alliances form, shaping policies worldwide. Exploring these complex relationships reveals how varied interests can converge, and if you keep exploring, you’ll uncover how these unlikely partnerships are changing the political landscape.
Key Takeaways
- Support for UBI spans unlikely political allies, including some conservative and progressive groups, despite traditional partisan divides.
- Economic debates about UBI often unite labor advocates and fiscal conservatives seeking poverty reduction and job flexibility.
- Cultural norms and societal attitudes create unexpected coalitions around UBI’s role in social cohesion and economic resilience.
- Pilot programs and research foster collaborations between government, academia, and community organizations across political lines.
- The global spread of UBI experiments demonstrates cross-national political alliances and unconventional support bases.
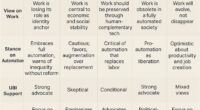
The Political Divide: Support and Opposition Across Party Lines

The political divide over Universal Basic Income (UBI) is pronounced, with Democrats showing strong support and Republicans largely opposing it. About 71% of Democrats favor UBI, while only 34% of Republicans agree. A significant majority of Republicans, 78%, oppose UBI, with 62% strongly against it. Support tends to be higher among younger Republicans, with 41% backing UBI, and lower-income voters across parties are more inclined to support it. Economic uncertainty and financial instability also influence opinions, making some Republicans more receptive. Meanwhile, middle and upper-income Republicans mostly oppose. The differences in party support stem from contrasting beliefs about government’s role in welfare and social responsibility, shaping the political landscape around UBI. Partisan and demographic support patterns show that support is higher among certain groups, such as younger adults and racial minorities, further highlighting the complex political landscape of UBI debates. Additionally, perceptions about government intervention and economic security play a crucial role in shaping these opinions, especially considering the potential impact on the economy, which remains a point of contention among critics and supporters alike. Understanding how public opinion shifts with economic conditions can provide deeper insight into future policy developments. Moreover, public perception of welfare programs influences the overall acceptance and skepticism toward UBI.
Demographic and Cultural Perspectives on UBI

Demographic and cultural factors heavily influence how people perceive and accept Universal Basic Income. You’ll find that:
Demographic and cultural influences shape public opinion and acceptance of Universal Basic Income across societies.
- Younger people tend to support UBI more, open to bold economic policies.
- Those with lower education levels often see UBI as a way to reduce poverty.
- Cultural norms shape opinions—some societies challenge UBI because it questions traditional work values. Additionally, social attitudes toward work and welfare greatly impact public support.
- Research shows that public opinion on UBI varies widely across countries and regions, often influenced by economic conditions and political discourse. Support varies widely depending on social context. For example, in cultures emphasizing personal responsibility, UBI might face skepticism. Conversely, countries with strong welfare histories often view it more favorably. Media narratives and historical backgrounds also shape perceptions, making acceptance complex. Recognizing these factors helps you understand why UBI’s popularity differs across demographics and cultures, highlighting that its political fate is deeply intertwined with societal values and norms. Additionally, the role of creative practice and innovative thinking in shaping policy debates can influence how UBI proposals are presented and received across different communities. Moreover, understanding community engagement strategies can improve public acceptance and foster more inclusive discussions about UBI. Furthermore, incorporating cultural context into policy design can enhance the legitimacy and effectiveness of UBI initiatives in diverse settings.
Economic Opportunities and Challenges of Basic Income

You might see UBI as a way to boost economic activity and reduce inequality, but funding it poses significant challenges that could require higher taxes. Some worry that providing a basic income might discourage people from working, while others argue it can encourage entrepreneurship and savings. Balancing these opportunities with potential drawbacks is essential to understanding UBI’s true economic impact. Additionally, implementing effective website functionality can be crucial for managing distributions and tracking outcomes efficiently. Ensuring transparent financial terms and jargon helps build public trust and comprehension of the program’s structure and goals. Clear communication about funding sources and budget allocation is vital for maintaining public support and ensuring program sustainability.
Cost and Funding Concerns
Implementing a universal basic income (UBI) involves significant costs and complex funding challenges that cannot be overlooked. You need to consider these key points:
- The estimated cost for UBI in the US could reach up to $3–4 trillion annually—about 75% of federal spending—making it a massive fiscal shift. This figure underscores the scale of financial commitment required.
- To lift everyone above the poverty line, costs drop to around $539 billion per year, less than 3% of GDP, but still a hefty investment. Exploring diverse funding options is crucial to ensure sustainability.
- Funding options include progressive taxes, natural resource revenues, or reallocating existing social programs, with some proposals suggesting administrative savings could help cover costs. Revenue generation methods are essential for maintaining program viability without overwhelming the economy or sacrificing essential services. Additionally, advancements in automation and AI could influence future economic stability and the availability of funding sources, as they may impact employment and income distribution. Moreover, understanding the personality traits of stakeholders involved can facilitate better communication and policy acceptance. Recognizing the role of retirement planning strategies such as IRAs and other savings vehicles can also help individuals prepare for economic changes and support overall financial resilience.
Work Incentive Debates
The debate over work incentives is central to evaluating the economic impact of universal basic income (UBI), as it raises questions about whether providing a guaranteed income might discourage people from working. Empirical evidence offers mixed results: some studies show fewer hours worked, while others report slight increases in employment. Policy design matters—if benefits taper off slowly as earnings rise, incentives stay stronger. Conditional UBI might better preserve motivation than unconditional models. Here’s how UBI influences work:
| Effect | Positive Impact | Potential Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Poverty Reduction | Encourages skill development | Reduces work hours in some cases |
| Entrepreneurial Drive | Supports startup risks | Possible dependence |
| Societal Attitudes | Promotes well-being and participation | May diminish work motivation |
| Employment Effects | The largest U.S. UBI trial showed a 2% decrease in labor participation, demonstrating potential work disincentives highlighting the importance of program design. |
Economic Stimulus Potential
Universal Basic Income (UBI) holds significant promise as an economic stimulus by directly injecting funds into household budgets, which can quickly boost consumer spending and aggregate demand. This rapid increase benefits the economy in several ways:
- Boosts consumption: Lower-income earners see the largest proportional gains, fueling demand across retail, services, and manufacturing.
- Supports GDP growth: Simulation models predict potential GDP increases, like 2.5% above baseline by 2035 with a well-funded UBI.
- Stabilizes during downturns: UBI can act as an automatic stabilizer, maintaining demand during recessions. By providing a safety net, UBI can help reduce economic volatility and prevent deep recessions. Economic stability Implementing UBI requires careful consideration of funding mechanisms and long-term sustainability. Additionally, payment processing solutions must be efficient, secure, and capable of handling large-scale distributions to ensure timely and reliable delivery of funds.
These effects can generate broad economic growth, create jobs, and stimulate various industries. However, inflation risks and funding challenges require careful policy design to guarantee sustainable benefits.
The Role of Pilot Programs and Research in Shaping Policy

Pilot programs and research play a crucial role in shaping basic income policy by providing real-world evidence of its potential impacts. Over 30 guaranteed income pilots are underway across the U.S., targeting diverse groups like unemployed individuals, low-income families, and specific communities. These pilots vary in design, payment structure, and conditions, often incorporating innovative elements like randomization and control groups. Rigorous research methods, such as randomized controlled trials, ensure reliable results across urban, rural, and suburban settings. Early findings suggest that basic income improves mental health, financial security, and life satisfaction, often with little negative impact on employment. Data from these pilots helps policymakers evaluate feasibility, costs, and benefits, guiding decisions on large-scale implementation and shaping the future of basic income policy.
Social Benefits and Community Impact of Universal Basic Income

Implementing a basic income can substantially transform communities by reducing poverty and promoting economic security. You’ll see immediate benefits like:
- Lower poverty rates: Consistent payments help eliminate extreme deprivation.
- Improved mental and physical health: Stable income reduces stress and boosts access to healthcare.
- Enhanced social cohesion: Income equality fosters trust and community engagement.
With UBI, you’ll notice less financial stress and greater autonomy over spending and savings. It can reduce welfare dependency and simplify social safety nets, cutting costs and stigma. Communities become more resilient, as local economies thrive through increased spending, savings, and entrepreneurship. Furthermore, social bonds strengthen as inequality diminishes, encouraging participation and reducing crime. Overall, UBI’s community impact creates healthier, more connected neighborhoods where everyone has a chance to thrive.
Advocacy, Legislation, and the Global Context of UBI
Advocacy efforts for UBI focus on highlighting its potential to reduce poverty, improve quality of life, and address economic inequality, especially as automation and AI threaten traditional jobs. Supporters push for pilot projects and increased public awareness to demonstrate benefits like better health, education, and wellbeing. They argue UBI can simplify welfare systems, cut bureaucracy, and reduce stigma. On the legislative front, bills like New York’s aim to exempt UBI from income tests, while countries like Ireland, Canada, and South Korea run pilot programs targeting vulnerable groups. Globally, over 160 pilots since the 1980s show promising results in reducing poverty but mixed effects on employment. Funding remains a challenge, with debates on taxation, reallocations, and sustainability, as governments balance economic feasibility with social benefits.

Despite growing interest in basic income, public perception remains a significant obstacle to advancing its adoption. You should know that:
- Public opinion shows over half oppose UBI, making widespread support difficult.
- Partisan divides deepen skepticism, with Democrats more supportive and Republicans largely opposed.
- Support has declined from 45% in 2020 to just 33% in 2023, reflecting shifting attitudes.
These perceptions are fueled by concerns over cost, economic impact, and work incentives. Public awareness remains limited, and media coverage often emphasizes negatives. To navigate this future, policymakers must focus on education, transparent funding models, and demonstrating UBI’s benefits for mental health and social welfare. Building consensus will require addressing fears and highlighting success stories to shift perceptions and political support.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does UBI Influence Mental Health and Overall Well-Being?
You might wonder how UBI impacts mental health and well-being. Evidence shows UBI can reduce anxiety and depression by providing income security, especially benefiting vulnerable groups like low-income individuals and women. When it supports, rather than replaces, work, mental health improves. However, long-term effects are uncertain, and outcomes depend on employment behaviors and policy design. Overall, UBI has the potential to enhance mental health and quality of life for many.
What Are the Environmental Impacts of Implementing UBI at Scale?
Think of UBI as a double-edged sword for the environment. When scaled up, it can promote greener choices, innovation, and reduce poverty’s strain on natural resources. But it might also spark more consumption, increasing emissions and resource use if not carefully managed. You’d need strong policies to steer the impact positively, ensuring the benefits outweigh the risks and that sustainability stays at the forefront.
Can UBI Reduce Income Inequality Effectively Across Diverse Regions?
You’re wondering if UBI can effectively reduce income inequality across different regions. The answer is yes, but its success depends on regional factors like economic conditions and existing social programs. You’ll see more impact in developing areas where UBI boosts empowerment, especially for marginalized groups. In advanced economies, UBI can help those facing wage stagnation. Overall, UBI’s universal nature helps narrow income gaps, but tailored approaches are essential for maximum effectiveness.
How Do Cultural Values Shape Public Acceptance of UBI?
Cultural values play a big role in how you see UBI. If your society highly values work and self-reliance, you might see UBI as a threat to those ideals. Conversely, if community support and fairness matter more, you’re more likely to accept UBI as a way to reduce inequality. Your trust in institutions and beliefs about effort and deservingness shape your attitude toward universal income programs.
What Legal Challenges Might UBI Face in Future Legislative Efforts?
Like Icarus flying too close to the sun, future UBI efforts face legal hurdles that could threaten their success. You’ll encounter challenges with existing laws, such as benefits cliffs and taxation, requiring complex legislative adjustments. Constitutional questions about federal versus state authority may stall progress. Plus, financing and work requirement debates could complicate passing laws, making the legal landscape as tricky as steering a labyrinth.
Conclusion
As you watch the landscape shift like clouds across a changing sky, remember that the fight for basic income is more than politics—it’s a battle for a fairer future. Whether you see it as a beacon of hope or a risky gamble, your voice shapes this evolving story. Stand at the crossroads, where diverse voices meet, and help steer society toward a horizon where everyone can find stability amid the shifting winds.